is diabetic ketoacidosis permanent Bhb test and diabetic ketoacidosis (dka)
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious, potentially life-threatening complication of diabetes. It occurs when there is a lack of insulin in the body, causing blood sugar levels to rise and ketones to build up. One of the most dangerous consequences of DKA is dehydration. In this post, we will explore why diabetic ketoacidosis causes dehydration and discuss its importance in the management of this condition.
Why Does Diabetic Ketoacidosis Cause Dehydration?
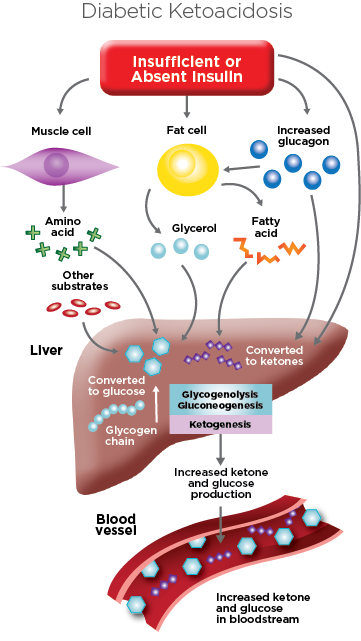
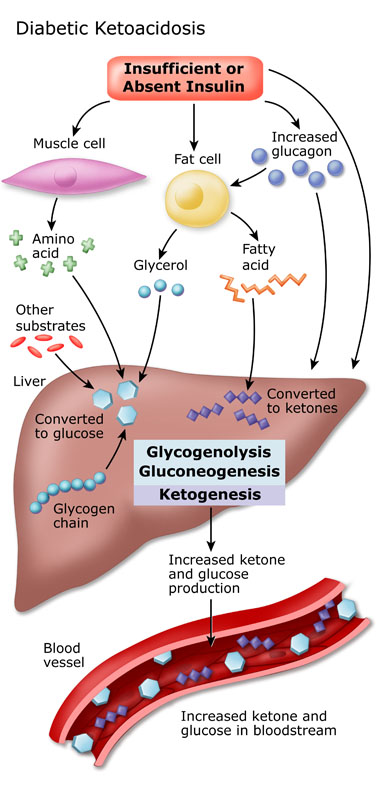
When the body lacks insulin, glucose cannot enter the cells to be used as fuel. As a result, the body starts breaking down fat for energy, which produces ketones as a byproduct. The accumulation of ketones in the blood leads to a condition known as ketoacidosis.
Ketoacidosis causes an increased production of urine, known as polyuria. This excessive urination results in the loss of large amounts of water and electrolytes from the body. If left untreated, the loss of water and electrolytes can lead to severe dehydration and electrolyte imbalances.
 Dehydration can be particularly dangerous in individuals with diabetes, as it can exacerbate the already high blood sugar levels associated with DKA. High blood sugar levels can further increase urine production, perpetuating the cycle of dehydration.
Dehydration can be particularly dangerous in individuals with diabetes, as it can exacerbate the already high blood sugar levels associated with DKA. High blood sugar levels can further increase urine production, perpetuating the cycle of dehydration.
Signs and Symptoms of Dehydration in DKA
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of dehydration is crucial in the management of DKA. Common signs of dehydration include:
- Excessive thirst
- Dry mouth and throat
- Dark urine or decreased urine output
- Weakness or fatigue
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Confusion or difficulty concentrating
 If you or someone you know with diabetes experiences any of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention immediately.
If you or someone you know with diabetes experiences any of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention immediately.
Managing Dehydration in DKA
The management of dehydration in DKA involves rehydrating the body and correcting electrolyte imbalances. This is typically done through intravenous (IV) fluids and electrolyte replacement under the supervision of healthcare professionals. The specific fluid and electrolyte composition used will depend on the individual’s needs and the severity of dehydration.
In addition to fluid replacement, the underlying cause of DKA, namely insulin deficiency, must be addressed. Insulin therapy is crucial in reversing the metabolic abnormalities associated with DKA, including dehydration. Intravenous insulin is often administered initially, followed by subcutaneous insulin once the individual’s condition stabilizes.
It is important to follow the healthcare professional’s instructions and attend regular medical check-ups to prevent future occurrences of DKA and dehydration. This may involve close monitoring of blood sugar levels, lifestyle modifications, and medication adjustments.
In conclusion, diabetic ketoacidosis causes dehydration due to the lack of insulin, which results in excessive loss of water and electrolytes through increased urine production. Dehydration can worsen the already high blood sugar levels associated with DKA and lead to severe complications if left untreated. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of dehydration and seeking prompt medical attention is essential in the management of DKA. Rehydration and addressing the underlying insulin deficiency are key components of DKA treatment. By understanding the relationship between DKA and dehydration, individuals with diabetes can take proactive steps to prevent and manage this potentially life-threatening complication.
If you are searching about Why Does Diabetic Ketoacidosis Cause Dehydration — DiabetesCareTalk.net you’ve came to the right web. We have 5 Pics about Why Does Diabetic Ketoacidosis Cause Dehydration — DiabetesCareTalk.net like Why Does Diabetic Ketoacidosis Cause Dehydration — DiabetesCareTalk.net, With Ketoacidosis Diabetes and also Diabetic Ketoacidosis Detailed Explanation within 7 minutes | Diabetic. Read more:
Why Does Diabetic Ketoacidosis Cause Dehydration — DiabetesCareTalk.net
 www.diabetescaretalk.netketoacidosis diabetic dka pathophysiology dehydration acidosis hyperglycemia mellitus hypoglycemia diabetestalk metabolic disambiguation hyperglycemic hyperosmolar
www.diabetescaretalk.netketoacidosis diabetic dka pathophysiology dehydration acidosis hyperglycemia mellitus hypoglycemia diabetestalk metabolic disambiguation hyperglycemic hyperosmolar
With Ketoacidosis Diabetes
 britishpropolis004.blogspot.comDiabetic Ketoacidosis Detailed Explanation Within 7 Minutes | Diabetic
britishpropolis004.blogspot.comDiabetic Ketoacidosis Detailed Explanation Within 7 Minutes | Diabetic
 www.pinterest.comketoacidosis diabetic explanation ketone bodies
www.pinterest.comketoacidosis diabetic explanation ketone bodies
BHB Test And Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) - EKF Diagnostics - Stanbio
 www.ekfusa.comketoacidosis hydroxybutyrate diabetic beta dka bhb test glucose blood insulin levels why liver illustration cells than
www.ekfusa.comketoacidosis hydroxybutyrate diabetic beta dka bhb test glucose blood insulin levels why liver illustration cells than
Pathophysiology Of Diabetic Ketoacidosis - Diabetic Ketoacidosis Is An
 ariadnehopkins.blogspot.comdiabetes ketoacidosis dka diabética aceite insulin cetoacidosis diabetica pathophysiology ucsf complication alzheimer stepwards ketones acidosis blood luchar dtc aceitedecoco rev1
ariadnehopkins.blogspot.comdiabetes ketoacidosis dka diabética aceite insulin cetoacidosis diabetica pathophysiology ucsf complication alzheimer stepwards ketones acidosis blood luchar dtc aceitedecoco rev1
Diabetic ketoacidosis detailed explanation within 7 minutes. Ketoacidosis hydroxybutyrate diabetic beta dka bhb test glucose blood insulin levels why liver illustration cells than. With ketoacidosis diabetes